PYELONEPHRITIS
pyelonephritis it is a bacterial infection of the kidney causing inflammation and in the word pyelonephritis itis means inflammation the prefix nephro means kidney and pilo refers to the renal pelvis which is this area of the kidney here acute Pyle nephritis is actually one of the more common conditions involving the kidney
EPIDEMIOLOGY
It occurs more often in females. The estimated annual rate of cases so for females, it's 15 to 17 cases per 10000 per year and that compares to three to four cases per 10 000 in males. The groups that are most at risk for getting acute piles of nephritis and patients with kidney stones have an increased risk of infection as well.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
let's talk about the pathophysiology of pyelonephritis. so there are actually two mechanisms of spread to the kidneys, one of them is through hematogenous spread. Hematogenous means it is spreading from the blood. This is actually an uncommon way that the kidney can be infected and it's more likely to occur in immunocompromised patients or patients with issues with their immune system. hematogenous spread is through the blood usually from another infection at a different site and that infection can get into the blood and that infection can go to the kidney through the bloodstream.
The second mechanism by which an infection can get to the kidneys and cause pyelonephritis is an ascending urinary tract infection. What happens is that there's a bacterial infection of the urethra so bacteria adhere to the urethra and slowly climb up the urethra once the bacteria reach the bladder this is classically known as a urinary tract infection we can call this cystitis as well so cystitis means inflammation of the bladder and then the bacteria can then continue to climb up. The ureters eventually lead to the kidneys which can lead to acute piles and nephritis.
WHY FEMALES ARE MORE AFFECTED?
In women, the urethra is shorter than in men so this is one reason why women are more at risk for having urinary tract infections in general but also having pyelonephritis because they have a shorter urethra so the bacteria don't have to climb as much to get into the system in general so that was a brief overview of the mechanism by which an ascending urinary tract infection can lead to acute pyelonephritis
CAUSE
It is a bacterial infection but more specifically the causes are generally gram-negative bacteria and the most common causative organism is E.coli which is a gram-negative rod. Other common causative organisms of acute pile nephritis include proteus bacteria, klebsiella, and Enterobacter.
SIGN & SYMPTOMS
Symptoms that often develop rather quickly over hours or over the course of a day and what we do find in this condition is the following
• fever and chills which makes sense this is an infection and it's an infection of the kidney.
• nausea and vomiting occurring
• anorexia so a loss of appetite
• and then we can also see symptoms of cystitis or symptoms of a urinary tract infection because most times acute pyelonephritis occurs by an ascending urinary tract infection and symptoms of a UTI include.
• urgency frequency
• and dysuria a burning sensation
• urgency
Atypical symptoms
• Epigastric pain is which occurs in the center of your abdomen above your belly button
SEVERE CASES
• Bacteremia so bacteria in the blood
• Sepsis and shock
• multiple organ system dysfunctions.
TYPES
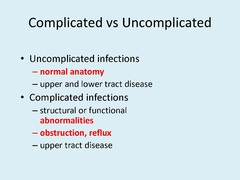
uncomplicated and complicated acute polynephritis is important because this can often determine whether a patient needs certain management or not
Uncomplicated acute pyelonephritis
It depends on patient characteristics
. Complicated acute polynephritis
If there are any of the following symptoms is present then it is called complicated acute polynephritis
• if the patient is pregnant
• if the patient has uncontrolled diabetes
• if the patient has kidney failure
• if they're immunocompromised.
• extremes of age
• male
DIAGNOSIS
Clinically it is diagnosed by
- Flank pain
- Costrovertebral angle tenderness
laboratory investigations are
Urinalysis. For a urinalysis, you will gather a pee test in an exceptional compartment at a specialist's office or at a lab. A medical care proficient will take a gander at the example under a magnifying instrument for microbes and white platelets, which the body produces to battle contamination. Microorganisms additionally can be found in the pee of solid individuals, so kidney contamination is analyzed and put together both with respect to your side effects and a lab test.
Urine culture. A medical care proficient may culture your pee to figure out what sort of microbes is causing the contamination. A medical services proficient can perceive how the microorganisms have increased, for the most part in 1 to 3 days, and can then decide the best therapy.
Imaging tests
A medical care proficient may utilize imaging tests, like a processed tomography (CT) examination, attractive reverberation imaging (MRI), or ultrasound, to assist with diagnosing kidney contamination. A specialist plays out these tests in a short-term community or an emergency clinic. A specialist might play out an ultrasound in a specialist's office also. A radiologist peruses and covers the pictures. You don't require sedation NIH outside interface for these tests. Peruse more imaging tests for your urinary plot.
TREATMENT
Rehydration is very important because these patients have issues with nausea and vomiting and they're not drinking a lot of fluids so, it's important to rehydrate them. Another treatment is antibiotics which are often taken for 7 to 14 days.
Oral fluoroquinolones can be used for ambulatory care or these oral antibiotics will be used for uncomplicated cases. If the case is complicated acute pile
nephritis it is done in hospitals. So, they've hospitalized patients and hospitalized patients will receive intravenous antibiotics. So, IV ceftriaxone may be an example, IV piptaseo may be an example, or IV fluoroquinolones. fluoroquinolones may be avoided as hospitalized patients may be started on some of these antibiotics and then once culture and sensitivities come back they will be narrowed. The spectrum will be narrowed to another antibiotic that is effective against that particular bacteria that is causing this infection.










0 Comments